Your Pathway to
Global IT Certification
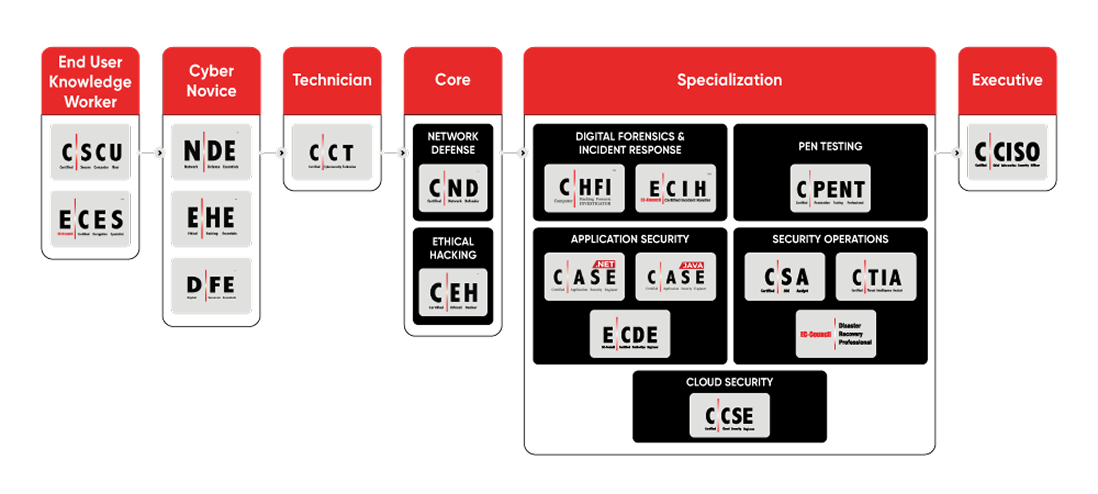
Empower Your Cybersecurity Career with Globally Recognized Certifications
The EC-Council is a globally recognized leader in cybersecurity education, best known for its Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) certification. Its training programs focus on practical, hands-on skills across ethical hacking, penetration testing, digital forensics, and security management—helping professionals detect, defend, and respond to modern cyber threats. At Mature Resources Global Technologies (MRGT), we deliver the complete suite of EC-Council certifications to support cybersecurity career paths from foundational knowledge to advanced technical roles. Whether you’re aiming to become a security analyst, engineer, or cyber leader, MRGT’s EC-Council trainings offer industry-recognized skills aligned with global security standards.
Ethical Hacking
Learn the tools and techniques hackers use and how to defend against them, with the industry-renowned CEH certification.
Certified Ethical Hacking (CEH)
Course Outline
- Module 01: Introduction to Ethical Hacking
Learn the fundamentals of key issues in the information security world, including the basics of ethical hacking, information security controls, relevant laws, and standard procedures.
Module 2: Foot Printing and Reconnaissance
Learn how to use the latest techniques and tools to perform foot printing and reconnaissance, a critical pre-attack phase of the ethical hacking process.
Module 3: Scanning Networks
Learn different network scanning techniques and countermeasures.
Module 4: Enumeration
Learn various enumeration techniques, including Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) and Network File Sharing (NFS) exploits and associated countermeasures.
Module 5: Vulnerability Analysis
Learn how to identify security loopholes in a target organization’s network, communication infrastructure, and end systems. Different types of vulnerability assessment and vulnerability assessment tools are included as well.
Module 6: System Hacking
Learn about the various system hacking methodologies used to discover system and network vulnerabilities, including steganography, steganalysis attacks, and how to cover tracks.
Module 7: Malware Threats
Learn about different types of malwares (Trojan, viruses, worms, etc.), APT and fileless malware, malware analysis procedures, and malware countermeasures.
Module 8: Sniffing
Learn about packet-sniffing techniques and their uses for discovering network vulnerabilities, plus countermeasures to defend against sniffing attacks.
Module 9: Social Engineering
Learn social engineering concepts and techniques, including how to identify theft attempts, audit human-level vulnerabilities, and suggest social engineering countermeasures.
Module 10: Denial-of-Service
Learn about different Denial of Service (DoS) and Distributed DoS (DDoS) attack techniques, plus the tools used to audit a target and devise DoS and DDoS countermeasures and protections.
Module 11: Session Hijacking
Learn the various session hijacking techniques used to discover network-level session management, authentication, authorization, and cryptographic weaknesses and associated countermeasures.
Module 12: Evading IDS, Firewalls, and Honeypots
Learn about firewall, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and honeypot evasion techniques; the tools used to audit a network perimeter for weaknesses; and countermeasures.
Module 13: Hacking Web Servers
Learn about web server attacks, including a comprehensive attack methodology used to audit vulnerabilities in web server infrastructures and countermeasures.
Module 14: Hacking Web Applications
Learn about web application attacks, including a comprehensive web application hacking methodology used to audit vulnerabilities in web applications and countermeasures.
Module 15: SQL Injection
Learn about SQL injection attack techniques, evasion techniques, and SQL injection countermeasures.
Module 16: Hacking Wireless Networks
Learn about different types of encryptions, threats, hacking methodologies, hacking tools, security tools, and countermeasures for wireless networks.
Module 17: Hacking Mobile Platforms
Learn mobile platform attack vectors, Android and iOS hacking, mobile device management, mobile security guidelines, and security tools.
Module 18: IoT and OT Hacking
Learn different types of Internets of Things (IoT) and operational technology (OT) attacks, hacking methodologies, hacking tools, and countermeasures.
Module 19: Cloud Computing
Learn different cloud computing concepts, such as container technologies and serverless computing, various cloud computing threats, attacks, hacking methodologies, and cloud security techniques and tools.
Module 20: Cryptography
Learn about encryption algorithms, cryptography tools, Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), email encryption, disk encryption, cryptography attacks, and cryptanalysis tools.
CEH Master
Course Outline
Module 01: Introduction to Ethical Hacking
Learn the fundamentals of key issues in the information security world, including the basics of ethical hacking, information security controls, relevant laws, and standard procedures.
Module 2: Foot Printing and Reconnaissance
Learn how to use the latest techniques and tools to perform foot printing and reconnaissance, a critical pre-attack phase of the ethical hacking process.
Module 3: Scanning Networks
Learn different network scanning techniques and countermeasures.
Module 4: Enumeration
Learn various enumeration techniques, including Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) and Network File Sharing (NFS) exploits and associated countermeasures.
Module 5: Vulnerability Analysis
Learn how to identify security loopholes in a target organization’s network, communication infrastructure, and end systems. Different types of vulnerability assessment and vulnerability assessment tools are included as well.
Module 6: System Hacking
Learn about the various system hacking methodologies used to discover system and network vulnerabilities, including steganography, steganalysis attacks, and how to cover tracks.
Module 7: Malware Threats
Learn about different types of malwares (Trojan, viruses, worms, etc.), APT and fileless malware, malware analysis procedures, and malware countermeasures.
Module 8: Sniffing
Learn about packet-sniffing techniques and their uses for discovering network vulnerabilities, plus countermeasures to defend against sniffing attacks.
Module 9: Social Engineering
Learn social engineering concepts and techniques, including how to identify theft attempts, audit human-level vulnerabilities, and suggest social engineering countermeasures.
Module 10: Denial-of-Service
Learn about different Denial of Service (DoS) and Distributed DoS (DDoS) attack techniques, plus the tools used to audit a target and devise DoS and DDoS countermeasures and protections.
Module 11: Session Hijacking
Learn the various session hijacking techniques used to discover network-level session management, authentication, authorization, and cryptographic weaknesses and associated countermeasures.
Module 12: Evading IDS, Firewalls, and Honeypots
Learn about firewall, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and honeypot evasion techniques; the tools used to audit a network perimeter for weaknesses; and countermeasures.
Module 13: Hacking Web Servers
Learn about web server attacks, including a comprehensive attack methodology used to audit vulnerabilities in web server infrastructures and countermeasures.
Module 14: Hacking Web Applications
Learn about web application attacks, including a comprehensive web application hacking methodology used to audit vulnerabilities in web applications and countermeasures.
Module 15: SQL Injection
Learn about SQL injection attack techniques, evasion techniques, and SQL injection countermeasures.
Module 16: Hacking Wireless Networks
Learn about different types of encryptions, threats, hacking methodologies, hacking tools, security tools, and countermeasures for wireless networks.
Module 17: Hacking Mobile Platforms
Learn mobile platform attack vectors, Android and iOS hacking, mobile device management, mobile security guidelines, and security tools.
Module 18: IoT and OT Hacking
Learn different types of Internets of Things (IoT) and operational technology (OT) attacks, hacking methodologies, hacking tools, and countermeasures.
Module 19: Cloud Computing
Learn different cloud computing concepts, such as container technologies and serverless computing, various cloud computing threats, attacks, hacking methodologies, and cloud security techniques and tools.
Module 20: Cryptography
Learn about encryption algorithms, cryptography tools, Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), email encryption, disk encryption, cryptography attacks, and cryptanalysis tools.
Pen Testing
Master advanced penetration testing methodologies to evaluate and secure networks, systems, and applications.
Certified Penetration Testing Professional (C|PENT)
Course Outline
- Module 01: Introduction to Penetration Testing & Methodologies
Module 02: Penetration Testing Scoping and Engagement
Module 03: Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT)
Module 04: Social Engineering Penetration Testing
Module 05: Network Penetration Testing – External
Module 06: Network Penetration Testing – Internal
Module 07: Network Penetration Testing – Perimeter Devices
Module 08: Web Application Penetration Testing
Module 09: Wireless Penetration Testing
Module 10: IoT Penetration Testing
Module 11: OT and SCADA Penetration Testing
Module 12: Cloud Penetration Testing
Module 13: Binary Analysis and Exploitation
Module 14: Report Writing and Post Testing Actions
Blockchain
Explore blockchain fundamentals, security implementation, and applications across industries.
Blockchain Developer Certification (B|DC)
Course Outline
- Module 01: Introduction to Blockchain Technology
Module 02: Cryptography and Technology
Module 03: Blockchain’s Impact on the Financial Sector
Module 04: Bitcoin
Module 05: Blockchain Project Implementation
Module 06: Security in Blockchain
Module 07: Cryptomining
Module 08: Ethereum
Module 09: Other Cryptocurrencies
Module 10: Artificial Intelligence and Blockchain
Module 11: Blockchain as a Service (BaaS)
Module 12: Open-Source Business Blockchain Frameworks
Module 13: Python for Blockchain
Module 14: JavaScript for Blockchain
Module 15: Java for Blockchain
Module 16: Blockchain Online Integrated Development Environments (IDEs)
Module 17: Industry Use Cases
Module 18: The Internet of Things and Blockchain
Module 19: Decentralized Applications (dApps)
Module 20: The Future of Blockchain
Module 21: Quantum Computing and Blockchain
Blockchain Fintech Certification (B|FC)
Course Outline
Module 01: Introduction
Module 02: Financial Applications
Module 03: Blockchain’s Cryptocurrency Assets
Module 04: Insurance Applications
Module 05: Blockchain Project Implementation
Module 06: Bitcoin
Module 07: Security in Blockchains
Module 08: Blockchain as a Service (BaaS)
Module 09: Ethereum
Module 10: Open Source
Module 11: Decentralized Applications (dApps)
Blockchain Business Leader Certification (B|BLC)
Course Outline
- Module 01: Introduction
Module 02: Financial Applications
Module 03: Blockchain’s Cryptocurrency Assets
Module 04: Blockchain Project Implementation
Module 05: Bitcoin
Module 06: Blockchain as a Service (BaaS)
Module 07: Security in Blockchains
Module 08: Ethereum
Module 09: Open Source
Module 10: Decentralized Apps (dApps)
Module 11: Scalable Blockchain
Module 12: Industry Use Cases
Module 13: The Internet of Things and Blockchain
Essentials Series
Build foundational knowledge in network defense, ethical hacking, and digital forensics for beginners.
Network Defense Essentials (N|DE)
Course Outline
- Module 01:Network Security Fundamentals
Module 02: Identification, Authentication, and Authorization
Module 03: Network Security Controls: Administrative Controls
Module 04: Network Security Controls: Physical Controls
Module 05: Network Security Controls: Technical Controls
Module 06: Virtualization and Cloud Computing
Module 07: Wireless Network Security
Module 08: Mobile Device Security
Module 09: IoT Device Security
Module 10: Cryptography and the Public Key Infrastructure
Module 11: Data Security
Module 12: Network Traffic Monitoring
Ethical Hacking Essentials (E|HE)
Course Outline
Module 01: Information Security Fundamentals
Module 02: Ethical Hacking Fundamentals
Module 03: Information Security Threats and Vulnerability Assessment
Module 04: Password Cracking Techniques and Countermeasures
Module 05: Social Engineering Techniques and Countermeasures
Module 06: Network Level Attacks and Countermeasures
Module 07: Web Application Attacks and Countermeasures
Module 08: Wireless Attacks and Countermeasures
Module 09: Mobile Attacks and Countermeasures
Module 10: IOT & OT Attacks and Countermeasures
Module 11: Cloud Computing Threats and Countermeasures
Module 12: Penetration Testing Fundamentals
Digital Forensic Essentials (D|FE)
Course Outline
- Module 01: Computer Forensics Fundamentals
Module 02: Computer Forensics Investigation Process
Module 03: Understanding Hard Disks and File Systems
Module 04: Data Acquisition and Duplication
Module 05: Defeating Anti-forensics Techniques
Module 06: Windows Forensics
Module 07: Linux and Mac Forensics
Module 08: Network Forensics
Module 09: Investigating Web Attacks
Module 10: Dark Web Forensics
Module 11: Investigating Email Crimes
Module 12: Malware Forensics
Executive Management
Gain strategic insights into cybersecurity leadership, governance, and risk management for executive roles.
Certified Chief Information Security Officer (C|CISO)
Incident Handling
Learn how to detect, manage, and respond to cybersecurity incidents and breaches effectively.
Certified Incident Handler (E|CIH)
Course Outline
- Module 01:Introduction to Incident Handling and Response
Module 02: Incident Handling and Response Process
Module 03: First Response
Module 04:Handling and Responding to Malware Incidents
Module 05:Handling and Responding to Email Security Incidents
Module 06:Handling and Responding to Network Security Incidents
Module 07: Handling and Responding to Web Application Security Incidents
Module 08:Handling and Responding to Cloud Security Incidents
Module 09:Handling and Responding to Insider Threats
Module 10:Handling and Responding to Endpoint security Incidents
Certified Threat Intelligence Analyst (C|TIA)
Course Outline
Module 01: Introduction to Threat Intelligence
- 1.1 Intelligence
- 1.2 Cyber Threat Intelligence Concepts
- 1.3 Threat Intelligence Lifecycle and Frameworks
- 1.4 Threat Intelligence Platforms (TIPs)
- 1.5 Threat Intelligence in the Cloud Environment
- 1.6 Future Trends and Continuous Learning
Key topics covered: Cyber Threat Intelligence, Threat Intelligence vs. Threat Data, Threat Intelligence vs. Traditional Cybersecurity Approaches, Types of Threat Intelligence, Threat Intelligence Generation, Responsibilities of Cyber Threat Analysts, Threat Intelligence Lifecycle, Threat Intelligence Strategy,Threat Intelligence Maturity Model, Threat Intelligence Frameworks, Threat Intelligence Platforms (TIPs), Role of Threat Intelligence in Cloud Security, and Career Paths and Opportunities in Threat Intelligence Field
Module 02: Cyber Threats and Attack Frameworks
- 2.1 Cyber Threats
- 2.2 Advanced Persistent Threats
- 2.3 Cyber Kill Chain
- 2.4 MITRE ATT&CK and Diamond Model
- 2.5 Indicators of Compromise
Key topics covered: Cyber Threats, Cyber Security Threat Categories, Threat Actors, Objectives of Cyber Security Attacks, Advanced Persistent Threats, Advanced Persistent Threat Lifecycle, Cyber Kill Chain Methodology, MITRE ATT&CK Framework, Diamond Model of Intrusion Analysis, Indicators of Compromise, Categories of Indicators of Compromise, and Pyramid of Pain
Module 03: Requirements, Planning, Direction, and Review
- 3.1 Organization’s Current Threat Landscape
- 3.2 Requirements Analysis
- 3.3 Plan a Threat Intelligence Program
- 3.4 Establish Management Support
- 3.5 Build a Threat Intelligence Team
- 3.6 Threat Intelligence Sharing
- 3.7 Review Threat Intelligence Program
Key topics covered: Identify Critical Threats to the Organization, Threat Intelligence Requirements, MoSCoW Method for Prioritizing Requirements, Scope of Threat Intelligence Program, Rules of Engagement, Threat Intelligence Program Planning, Project Charter and Policy Preparation, Threat Intelligence Roles and Responsibilities, Build Intelligence Team, Threat Intelligence Sharing, Types of Sharing Partners, and Threat Intelligence-led Engagement Review
Module 04: Data Collection and Processing
- 4.1 Threat Intelligence Data Collection
- 4.2 Threat Intelligence Collection Management
- 4.3 Threat Intelligence Feeds and Sources
- 4.4 Threat Intelligence Data Collection and Acquisition
- 4.5 Bulk Data Collection
- 4.6 Data Processing and Exploitation
- 4.7 Threat Data Collection and Enrichment in Cloud Environments
Labs
- Data Collection through Search Engines, Web Services, Website Footprinting, Email Footprinting, DNS Interrogation, Automated OSINT Tools, Social Engineering Techniques, Cyber Counterintelligence (CCI) Techniques, Malware Analysis, and Python Scripting
- IoC Data Collection through External Sources and Internal Sources
- Structuring/Normalization of Collected Data
Key topics covered: Threat Intelligence Data Collection, Data Collection Methods, Types of Data, Types of Threat Intelligence Data Collection, Threat Intelligence Collection Plan, Threat Intelligence Feeds, Threat Intelligence Sources, Threat Intelligence Data Collection and Acquisition, Data Collection through Python Scripting, Bulk Data Collection, Bulk Data Management, Data Processing and Exploitation, Structuring/Normalization of Collected Data, Data Sampling, and Threat Data Collection in Cloud Environments Module 05: Data Analysis
- 5.1 Data Analysis
- 5.2 Data Analysis Techniques
- 5.3 Threat Analysis
- 5.4 Threat Analysis Process
- 5.5 Fine-Tuning Threat Analysis
- 5.6 Threat Intelligence Evaluation
- 5.7 Create Runbooks and Knowledge Base
- 5.8 Threat Intelligence Tools
Labs:
- Perform Threat Modeling and Data Analysis
- Perform Complete Threat Intelligence using Threat Intelligence Tools
Key topics covered: Data Analysis, Types of Data Analysis, Statistical Data Analysis, Analysis of Competing Hypotheses (ACH), Structured Analysis of Competing Hypotheses (SACH), Threat Analysis, Types of Threat Intelligence Analysis, Threat Analysis Process, Threat Modeling Methodologies, Threat Analysis Process with Diamond Model Framework, Validating and Prioritizing Threat Indicators, Fine-Tuning Threat Analysis, Automate Threat Analysis Processes, Threat Intelligence Evaluation, Threat Attribution, Creating Runbooks, Threat Knowledge Base, and Threat Intelligence Tools
Module 06: Intelligence Reporting and Dissemination
- 6.1 Threat Intelligence Reports
- 6.2 Dissemination
- 6.3 Participate in Sharing Relationships
- 6.4 Sharing Threat Intelligence
- 6.5 Delivery Mechanisms
- 6.6 Threat Intelligence Sharing Platforms
- 6.7 Intelligence Sharing Acts and Regulations
- 6.8 Threat Intelligence Integration
- 6.9 Threat Intelligence Sharing and Collaboration using Python Scripting
Labs:
- Perform Threat Intelligence Reporting and Sharing
Key topics covered: Threat Intelligence Reports, Types of Cyber Threat Intelligence Reports, Report Writing Tools, Dissemination, Threat Intelligence Sharing, Information Sharing Model, Information Exchange Types, Sharing Community, Sharing Intelligence using YARA Rules, Standards and Formats for Sharing Threat Intelligence, Information Sharing and Collaboration Platforms, Intelligence Sharing Acts and Regulations, Threat Intelligence Integration, Threat Intelligence Sharing using Python Scripting
Module 07: Threat Hunting and Detection
- 7.1 Threat Hunting Concepts
- 7.2 Threat Hunting Automation
Labs:
- Perform Targeted Threat Hunting using Python Scripts
- Perform Threat Hunting Automation using Threat Intelligence Tools
Key topics covered: Threat Hunting, Types of Threat Hunting, Threat Hunting Process, Threat Hunting Maturity Model (HMM), Threat Hunter Skillset, Threat Hunting Loop, Targeted Hunting Integrating Threat Intelligence (TaHiTI), Threat Hunting Automation, and Threat Hunting Automation using Python Scripting
Module 08: Threat Intelligence in SOC Operations, Incident Response, and Risk Management
- 8.1 Threat Intelligence in SOC Operations
- 8.2 Threat Intelligence in Risk Management
- 8.3 Threat Intelligence in Incident Response
Labs:
- Perform Cyber Threat Intelligence using the SOC Threat Intelligence Platforms
Key topics covered: Threat Intelligence in SOC Operations, Building SOC Threat Intelligence, Next-Gen Intelligent SOC, SOC Threat Intelligence Platforms (TIPs), Threat Intelligence in Risk Management Process, Integrating Threat Intelligence into Risk Management Processes, Threat Intelligence into the Incident Response Process, and Threat Intelligence in Incident Recovery and Resilience
Certified SOC Analyst (C|SA)
Course Outline
- Module 1: Security Operations and Management
Module 2: Understanding Cyber Threats, IoCs, and Attack Methodology
Module 3: Incidents, Events, and Logging
Module 4: Incident Detection with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
Module 5: Enhanced Incident Detection with Threat Intelligence
Module 6: Incident Response
Business Continuity & Disaster Recovery
Understand how to plan for, mitigate, and recover from disruptions to ensure organizational resilience.
Disaster Recovery Professional (E|DRP)
Course Outline
- Access systems and get help: Log in to local and remote Linux systems, and investigate problem resolution methods provided through Red Hat Insights and support.
- Navigate file systems: Copy, move, create, delete, and organize files while working from the bash shell.
- Manage local users and groups: Create, manage, and delete local users and groups and administer local password policies.
- Control access to files: Set Linux file system permissions on files and to interpret the security effects of different permission settings.
- Manage SELinux security: Protect and manage the security of a server by using SELinux.
- Tune system performance: Evaluate and control processes, set tuning parameters, and adjust process scheduling priorities on a Red Hat Enterprise Linux system.
- Install and update software packages: Download, install, update, and manage software packages from Red Hat and DNF package repositories.
- Manage basic storage: Create and manage storage devices, partitions, file systems, and swap spaces from the command line.
- Control services and the boot process: Control and monitor network services, system daemons, and the boot process using systemd.
- Manage networking: Configure network interfaces and settings on Red Hat Enterprise Linux servers.
- Analyze and store logs: Locate and accurately interpret logs of system events for troubleshooting purposes.
- Implement advanced storage features: Create and manage logical volumes containing file systems and swap spaces from the command line, and configure advanced storage features with Stratis and VDO.
- Schedule future tasks: Schedule tasks to automatically execute in the future.
- Access network-attached storage: Access network-attached storage, using the NFS protocol.
- Manage network security: Control network connections to services using the system firewall and SELinux rules.
- Running Containers: Obtain, run, and manage simple, lightweight services as containers on a single Red Hat Enterprise Linux server.
Application Security
Dive into securing applications against vulnerabilities throughout the development lifecycle.
Certified Application Security Engineer (C|ASE.NET)
Course Outline
- Module 01:Understanding Application Security, Threats, and Attacks
Module 02: Security Requirements Gathering
Module 03: Secure Application Design and Architecture
Module 04: Secure Coding Practices for Input Validation
Module 05: Secure Coding Practices for Authentication and Authorization
Module 06: Secure Coding Practices for Cryptography
Module 07: Secure Coding Practices for Session Management
Module 08: Secure Coding Practices for Error Handling
Module 09: Static and Dynamic Application Security Testing (SAST & DAST)
Module 10: Secure Deployment and Maintenance
Certified Application Security Engineer (C|ASE Java)
Course Outline
Module 01:Understanding Application Security, Threats, and Attacks
Module 02: Security Requirements Gathering
Module 03: Secure Application Design and Architecture
Module 04: Secure Coding Practices for Input Validation
Module 05: Secure Coding Practices for Authentication and Authorization
Module 06: Secure Coding Practices for Cryptography
Module 07: Secure Coding Practices for Session Management
Module 08: Secure Coding Practices for Error Handling
Module 09: Static and Dynamic Application Security Testing (SAST & DAST)
Module 10: Secure Deployment and Maintenance
Web Application Hacking & Security
Course Outline
Computer Forensics
Acquire skills in digital evidence collection, analysis, and legal procedures in cybercrime investigations.
Computer Hacking Forensic Investigator (C|HFI)
Course Outline
- Module 01: Computer Forensics in Today’s World
Module 02: Computer Forensics Investigation Process
Module 03: Understanding Hard Disks and File Systems
Module 04: Data Acquisition and Duplication
Module 05: Defeating Anti-Forensics Techniques
Module 06: Windows Forensics
Module 07: Linux and Mac Forensics
Module 08: Network Forensics
Module 09: Investigating Web Attacks
Module 10: Dark Web Forensics
Module 11: Database Forensics
Module 12: Cloud Forensics
Module 13: Investigating Email Crimes
Module 14: Malware Forensics
Module 15: Mobile Forensics
Module 16: IoT Forensics
Cloud Security
Learn to secure cloud infrastructure, applications, and services across hybrid and public cloud environments.
Certified Cloud Security Engineer (C|CSE)
Course Outline
- Module 01: Introduction to Cloud Security
Module 02: Platform and Infrastructure Security in the Cloud
Module 03: Application Security in the Cloud
Module 04: Data Security in the Cloud
Module 05: Operation Security in the Cloud
Module 06: Penetration Testing in the Cloud
Module 07: Incident Detection and Response in the Cloud
Module 08: Forensics Investigation in the Cloud
Module 09: Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery in the Cloud
Module 10: Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance in the Cloud
Module 11: Standards, Policies, and Legal Issues in the Cloud
Fundamentals
Get introduced to key cybersecurity concepts and career paths, ideal for newcomers to the field.
Certified Secure Computer User (C|SCU)
Course Outline
- Module 1: Introduction to Data Security
Module 2: Securing Operating Systems
Module 3: Malware and Antivirus
Module 4: Internet Security
Module 5: Security on Social Networking Sites
Module 6: Securing Email Communications
Module 7: Securing Mobile Devices
Module 8: Securing the Cloud
Module 9: Securing Network Connections
Module 10: Data Backup and Disaster Recovery
Module 11: Securing IOT Devices & Gaming Console
Module 11: Securing IOT Devices & Gaming Console
Module 12: Secure Remote Work
Ec-Council Certified Security Specialist(E|CSS)
Course Outline
Network Defense Essentials
Network Security Fundamentals
Identification, Authentication, and Authorization
Network Security Controls: Administrative Controls
Network Security Controls: Physical Controls
Network Security Controls: Technical Controls
Virtualization and Cloud Computing
Wireless Network Security
Mobile Device Security
IoT Device Security
Cryptography and the Public Key
Data Security
Network Traffic Monitoring
Ethical Hacking Essentials
Information Security Fundamentals
Ethical Hacking Fundamentals
Information Security Threats and Vulnerability
Password Cracking and Countermeasures
Social Engineering and Countermeasures
Network Level Attacks and Countermeasures
Web Application Attacks and Countermeasures
Wireless Attacks and Countermeasures
Mobile Attacks and Countermeasures
IOT & OT Attacks and Countermeasures
Cloud Computing Threats and Countermeasures
Penetration Testing Fundamentals
Digital Forensics Essentials
Computer Forensics Fundamentals
Computer Forensics Investigation Process
Understanding Hard Disks and File Systems
Data Acquisition and Duplication
Defeating Anti-forensics Techniques
Windows Forensics
Linux and Mac Forensics
Network Forensics
Investigating Web Attacks
Dark Web Forensics
Investigating Email Crimes
Malware Forensics
Network Security
Gain expertise in protecting enterprise networks from intrusions, malware, and other threats.
Certified Network Defender (CND)
Course Outline
- Module 01: Network Attacks and Defense Strategies
Module 02: Administrative Network Security
Module 03: Technical Network Security
Module 04: Network Perimeter Security
Module 05: Endpoint Security-Windows Systems
Module 06: Endpoint Security-Linux Systems
Module 07: Endpoint Security- Mobile Devices
Module 08: Endpoint Security-IoT Devices
Module 09: Administrative Application Security
Module 10: Data Security
Module 11: Enterprise Virtual Network Security
Module 12: Enterprise Cloud Network Security
Module 13: Enterprise Wireless Network Security
Module 14: Network Traffic Monitoring and Analysis
Module 15: Network Logs Monitoring and Analysis
Module 16: Incident Response and Forensic Investigation
Module 17: Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
Module 18: Risk Anticipation with Risk Management
Module 19: Threat Assessment with Attack Surface Analysis
Module 20: Threat Prediction with Cyber Threat Intelligence
DevSecOps
Integrate security into DevOps workflows to build secure, automated, and resilient systems.
Certified DevSecOps Engineer (E|CDE)
Course Outline
- Module 01: Understanding DevOps Culture
Module 02: Introduction to DevSecOps
Module 03: DevSecOps Pipeline—Plan Stage
Module 04: DevSecOps Pipeline—Code Stage
Module 05: DevSecOps Pipeline—Build and Test Stage
Module 06: DevSecOps Pipeline—Release and Deploy Stage
Module 07: DevSecOps Pipeline—Operate and Monitor Stage
Encryption
Understand cryptographic protocols, encryption techniques, and their real-world applications in data protection.
Certified Encryption Specialist (E|CES)
Course Outline
- Module 1: Introduction and History of Cryptography
Key Topics: Overview of Cryptography, Understanding Mono-Alphabet Substitution Cryptographic Algorithms, Understanding Multi-Alphabet Substitution Cryptographic Algorithms, Understanding Homophonic Substitution Cryptographic Algorithms
Module 2: Symmetric Cryptography and Hashes
Key Topics: Overview of Symmetric Cryptography, Understanding Basic Binary Math in Cryptography, Understanding Symmetric Block Cipher Algorithms, Understanding Symmetric Algorithm Methods, Overview of Symmetric Stream Ciphers, Overview of Cryptographic Hash Algorithms
Module 3: Number Theory and Asymmetric Cryptography
Key Topics: Overview of Asymmetric Cryptography, Understanding Basic Number Facts, Understanding Birthday Theorem, Understanding Random Number Generators, Overview of Asymmetric Encryption Algorithms
Module 4: Applications of Cryptography
Key Topics: Overview of Digital Signatures, Digital Certificates, and Digital Certificate Management, Understanding Authentication Protocols, Understanding Wi-Fi Encryption, SSL, and TLS, Understanding VPN and Protocols Used to Create VPN, Understanding File and Disk Encryption, Overview of Steganography and Steganalysis, Overview of National Security Agency Encryption Algorithms
Module 5: Cryptanalysis
Key Topics: Overview of Cryptanalysis, Understanding Cryptanalysis Techniques, Overview of Cryptanalysis Resources and Success, Understanding Password Cracking.
Cyber Technician
Train as a hands-on cyber technician equipped with practical skills across multiple domains of cybersecurity.
Certified Cybersecurity Technician (C|CT)
Course Outline
- Module 01: Information Security Threats and Vulnerabilities
Module 02: Information Security Attacks
Module 03: Network Security Fundamentals
Module 04: Identification, Authentication, and Authorization
Module 05: Network Security Controls – Administrative Controls
Module 06: Network Security Controls – Physical Controls
Module 07: Network Security Controls – Technical Controls
Module 08: Network Security Assessment Techniques and Tools
Module 09: Application Security
Module 10: Virtualization and Cloud Computing
Module 11: Wireless Network Security
Module 12: Mobile Device Security
Module 13: IoT and OT Security
Module 14: Cryptography
Module 15: Data Security
Module 16: Network Troubleshooting
Module 17: Network Traffic Monitoring
Module 18: Network Logs Monitoring and Analysis
Module 19: Incident Response
Module 20: Computer Forensics
Module 21: Business Continuity and Disaster Recoverys
Module 22: Risk Management
Start your Training Today!
Jumpstart your future with in-demand tech skills. Submit your details and our team will get in touch to guide you through the next steps.